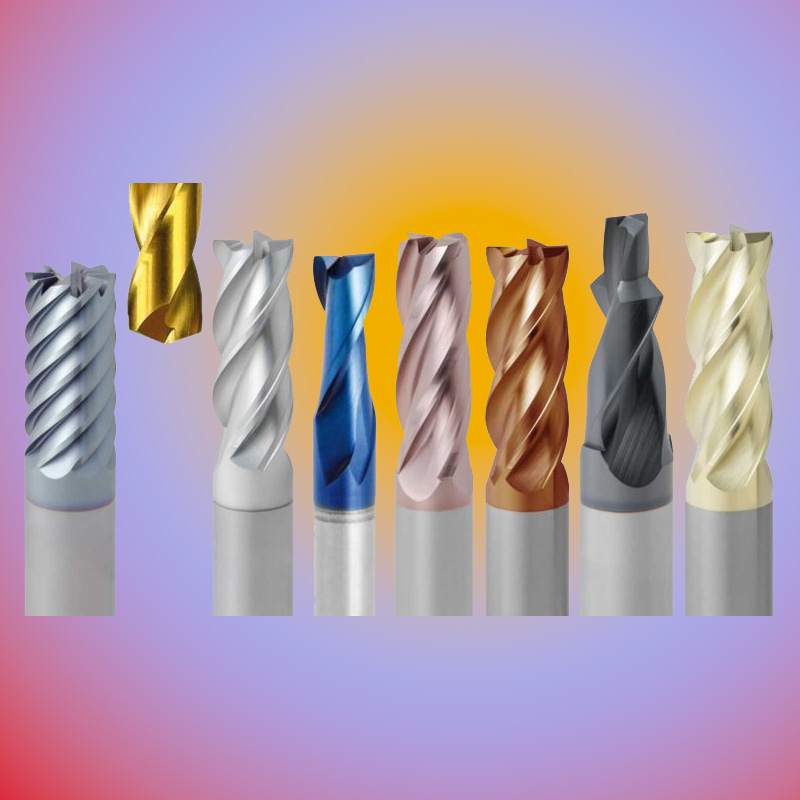
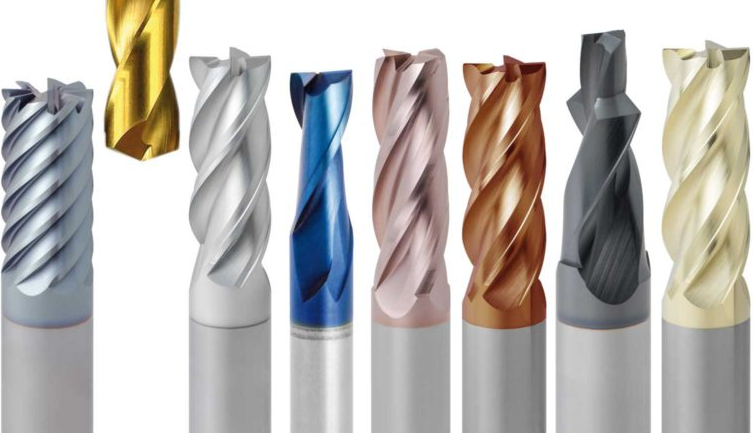
Our Business goal is to assist customers for their pro- ductivity improvement coupled with reduced
tooling cost.
Call Us Today
+91-99447 96108
Working Hours
Monday-Saturday : 9.00AM to 8.00PM
237-M, LIC colony, (Kumar tower opp),
Sidco post Coimbatore-641021.
Coating
Cutting tool materials have different combinations of hardness, toughness and wear resistance, and are divided into numerous grades with specific properties. Generally, a cutting tool material that is successful in its application should be:
- Hard, to resist flank wear and deformation
- Tough, to resist bulk breakage
- Non-reactive with the workpiece material
- Chemically stable, to resist oxidation and diffusion
- Resistant to sudden thermal changes
Advatages
- Good mechanical and cutting performance: The coated metal cutting tools combines the excellent performance of the base material and the coating material, which not only maintains the good toughness and high strength of the base, but also has the high hardness, high wear resistance and low resistance of the coating, coefficient of friction. Therefore, the cutting speed of the coated tool can be increased by more than 2 times than that of the uncoated tool, and a higher feed rate is allowed, and its life has also been improved.
- Strong versatility: The coated tools has wide versatility and the processing range is significantly expanded. One type of coated tool can replace several types of uncoated tools.
- Thickness of coating: The tool life will increase with the increase of coating thickness, but when the coating thickness reaches saturation, the tool life will no longer increase significantly. When the coating is too thick, it is easy to cause peeling; when the coating is too thin, the wear resistance is poor.
- Regrind ability: poor regrind ability of coated blades, complex coating equipment, high process requirements, and long coating time.
- Coating materials: cutting tools with different coating materials have different cutting performance. For example, when cutting at low speed, TiC coating has an advantage; when cutting at high speed, TiN is more suitable.